How MoS2 Works as a Lubricant: Mechanism Explained
- Home
- How MoS2 Works as a Lubricant: Mechanism Explained
What is MoS2: How MoS2 Works as a Lubricant
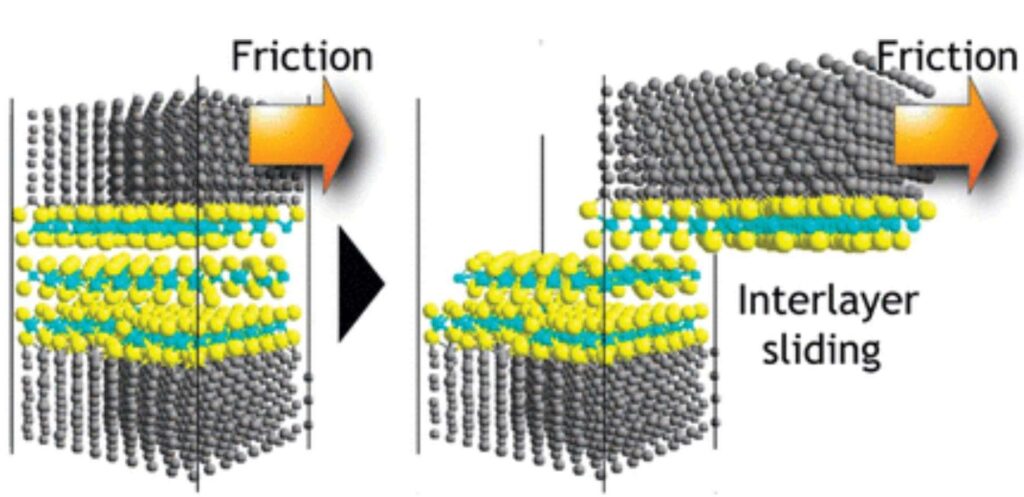
Molybdenum Di Sulfide or MoS2 is a layered material, with each layer consisting of a nano thin sheet of molybdenum atoms which are sandwiched between two nano sheets of sulfur atoms. The layers are held together by weak van der Waals forces, allowing them to easily slide over each other.

Formation of Boundary Lubricating Films:
During working of bearing (rolling or sliding), the MoS2 layers are transferred to the metal surfaces of bearing in contact. The Transfer can be through coating or applying grease. As the components move, these transferred layers form a solid boundary lubricating film on the metal surfaces. This film provides a protective barrier between the metal parts and minimizes direct metal-to-metal contact.
What are the challenges of lubrication (Liquid and grease)?
- Temperature Extremes
- Weight and Space Constraints
- Risk of Leakage
- Maintenance Requirements
- Contamination
- Environmental Concerns
- Complex Systems
- Incompatibility
- Grease Migration
What is the best way to use MoS2 as lubricant?
Solid Lubrication coating of nano sized MoS2 on bearing components.
MoS2 is a dry lubricant, which means it doesn’t require the continuous application of liquid or grease lubricants. This feature reduces the need for maintenance and minimizes the risk of contamination in aerospace application applications.
Using solid MoS2 coatings eliminates the risk of leakage or spillage associated with traditional liquid lubricants, making it an environmentally friendly choice. It also reduces maintenance and cleanup requirements.
MoS2 retains its lubricating properties even at extreme temperatures makes the best choice for aerospace
The coating thickness can be controlled precisely all over the surface making a uniform coating. Best choice for high speed bearings
| Lubrication boundary condition/ application | Coating variables can be tuned |
| No-Slip Boundary Condition | Coating Adhesion – base metal surface finish to particle size balance |
| Pressure Distribution | Centrifuging rate – uniform film formation during coating by hydrothermal soft chemical route method |
| Temperature Distribution | Control Surface/ Volume Ratio of MoS2 Nano particle |
| Viscosity and Shear Rate | Surface hardness and toughness tuning of coating by calibrating the chemical composition ratio |
| Surface Roughness | Increasing hardness of coating |
| Replenishment Rate | Controlling thickness of coating as per application |
| Chemical and Environmental Conditions | Controlling acidic & basic behavior of the compound |



Leave A Comment